Early Signs and Causes of Oral (Mouth) Cancer
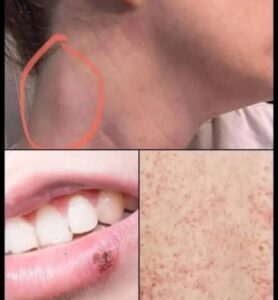
Oral cancer, often referred to as mouth cancer, is a serious condition that develops in the tissues of the mouth and throat. In many medical studies, it is grouped under head and neck cancers, since it commonly arises in the tongue, lips, gums, or the lining of the cheeks.
Most cases are diagnosed in people over the age of 40, and research shows that men face a slightly higher risk compared to women. While oral cancer can occur anywhere in the world, it is a major public health concern in South Asia. In India alone, over 77,000 new cases were registered in a single year, with more than 52,000 deaths reported—highlighting the urgent need for awareness, prevention, and early detection.
Why Early Detection Matters
Mouth cancer often goes unnoticed in its earliest stages because symptoms can seem harmless or similar to everyday mouth problems. However, once the disease spreads to the lymph nodes in the neck, treatment becomes more complex. Detecting it early greatly improves the chances of recovery, reduces treatment intensity, and lowers long-term risks.
Common Risk Factors
Experts have identified several lifestyle and environmental factors that increase the risk of developing oral cancer. Some of the most significant include:
-
Tobacco use: Whether smoked (cigarettes, cigars, pipes) or chewed in forms such as betel quid or gutka, tobacco is one of the leading causes.
-
Excessive alcohol consumption: Drinking large amounts of alcohol regularly can irritate the tissues of the mouth and throat, raising cancer risk.
-
Poor oral hygiene: Chronic infections, untreated dental issues, and poor gum health may contribute to long-term complications.
-
Diet low in fruits and vegetables: A lack of protective antioxidants and vitamins can weaken the body’s ability to repair damaged cells.
-
Exposure to HPV (Human Papillomavirus): Certain strains of this virus have been linked to oropharyngeal cancers.
-
Prolonged sun exposure: Increases the risk of lip cancer, especially in outdoor workers without protection.
Possible Warning Signs
While not every symptom indicates cancer, some early warning signs should not be ignored:
-
Persistent mouth ulcers or sores that do not heal
-
Unexplained lumps or thickened patches in the mouth or throat
-
Red or white patches inside the mouth
-
Difficulty chewing, swallowing, or moving the jaw
-
Persistent pain in the mouth or ear without clear cause
-
Swelling in the jaw or neck
If these symptoms last for more than two weeks, a consultation with a healthcare professional is strongly advised.
Prevention and Awareness
The good news is that oral cancer is largely preventable. By avoiding high-risk behaviors such as tobacco use and heavy drinking, maintaining good oral hygiene, and adopting a diet rich in fruits and vegetables, individuals can significantly lower their risk. Regular dental check-ups also play a key role, as dentists are often the first to spot suspicious changes in the mouth.
Public health campaigns continue to emphasize the importance of awareness, especially in regions where chewing tobacco is common. Simple lifestyle changes and early screenings can save thousands of lives each year.
Final Thoughts
Mouth cancer remains a serious global health issue, but one that can be managed—and often prevented—through awareness, healthy living, and timely medical care. By learning to recognize the signs and understanding the causes, individuals can take proactive steps toward protecting their health.